Materiality (Important Challenges)
Mitsubishi Electric Group’s Materiality
To address sustainability at the management level and ensure long-term commitment, the Mitsubishi Electric Group has identified five areas as materiality (important challenges) to “Provide solutions to social challenges through our businesses” and to “Strengthen our business foundation to enable sustainable growth.” The Group is taking a “Trade-On (mutual benefits)” approach to realizing sustainability by implementing materiality initiatives to create business solutions for social challenges while securing its own business growth at the same time. For our materiality initiatives, we set targets and key performance indicators (KPIs) and carry out continuous improvement activities using the PDCA cycle.
 Materiality at the Mitsubishi Electric Group
Materiality at the Mitsubishi Electric Group
Materiality and SDGs
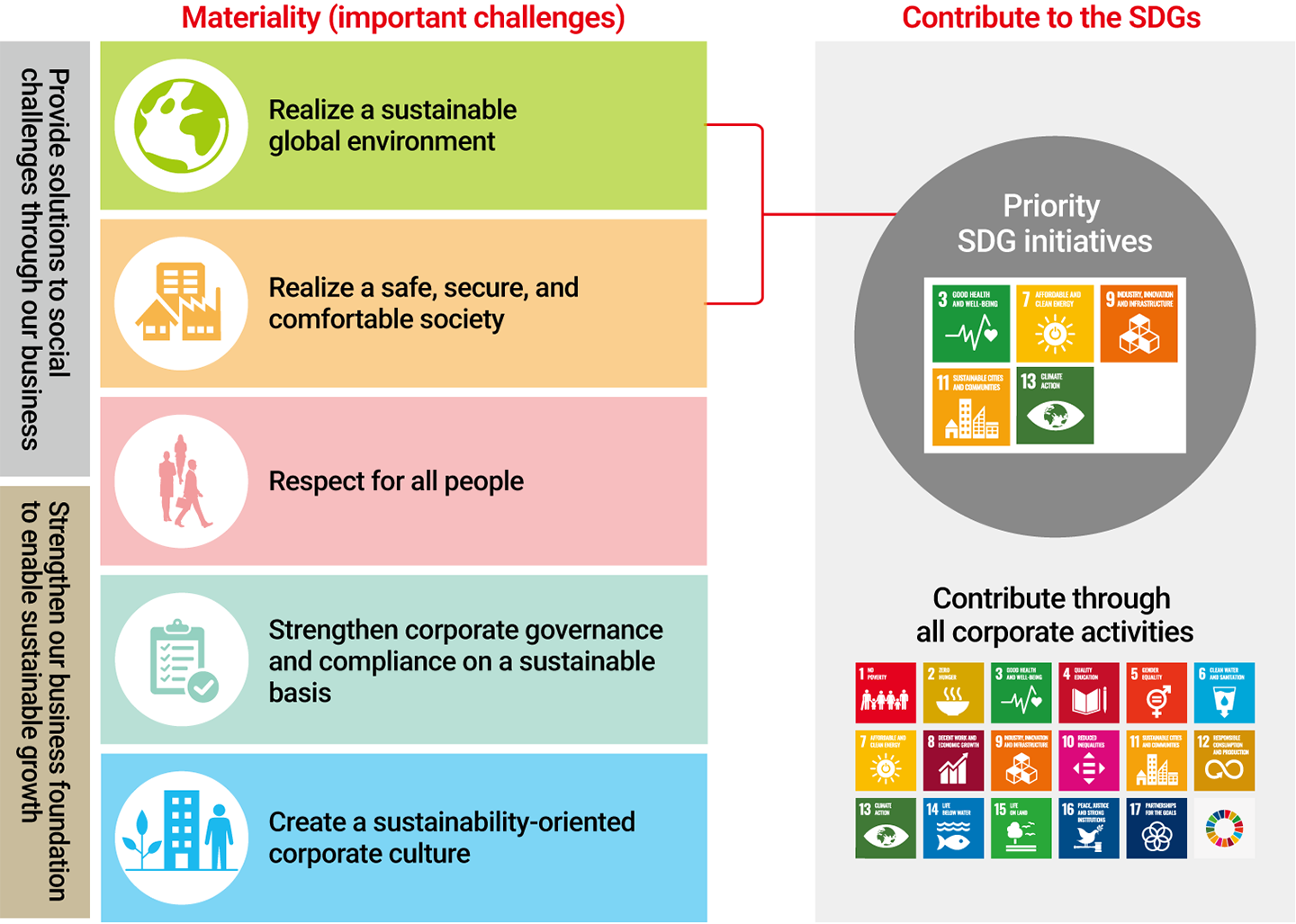
Under its Purpose that “We, the Mitsubishi Electric Group, will contribute to the realization of a vibrant and sustainable society through continuous technological innovation and ceaseless creativity, ” the Group aims to contribute to solving social issues by implementing the five areas of materiality issues. This policy aligns with the objectives of the globally shared SDGs.*
As a comprehensive electrical and electronics manufacturer with a broad portfolio of technologies, products, and services, we recognize our significant potential to contribute to the achievement of all 17 SDGs through our diverse business operations and our ongoing commitment to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) initiatives.
In particular, we revised our Priority SDGs initiatives in conjunction with the identification of materiality issues (important challenges) in fiscal 2021. An internal survey regarding our contributions to the SDGs revealed strong expectations for the Group to provide solutions to social challenges through our businesses. Based on these findings, we designated five SDGs as Priority SDGs initiatives: Goal 3 (Good Health and Well-being), Goal 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy), Goal 9 (Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure), Goal 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities), and Goal 13 (Climate Action). These goals reflect the Group’s commitment to realizing a sustainable global environment and a safe, secure, and comfortable society.
- Sustainable Development Goals
 Materiality and SDGs
Materiality and SDGs
Process of Identification and Review of Materiality
In fiscal 2016, the Mitsubishi Electric Group identified materiality and initiatives in response to today’s social trends and business environment, as required by the fourth edition of the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) Guidelines.
In fiscal 2021, a full internal review of the materiality, mid- to long-term initiatives, and targets/key performance indicators (KPIs) was conducted. This review involved subjective evaluations from both inside and outside the company, along with questionnaires and interviews with a total of 1,551 participants, including Mitsubishi Electric Group employees, suppliers, investors, analysts, and general consumers.
Step 1 Awareness of Social Issues (FY2021)
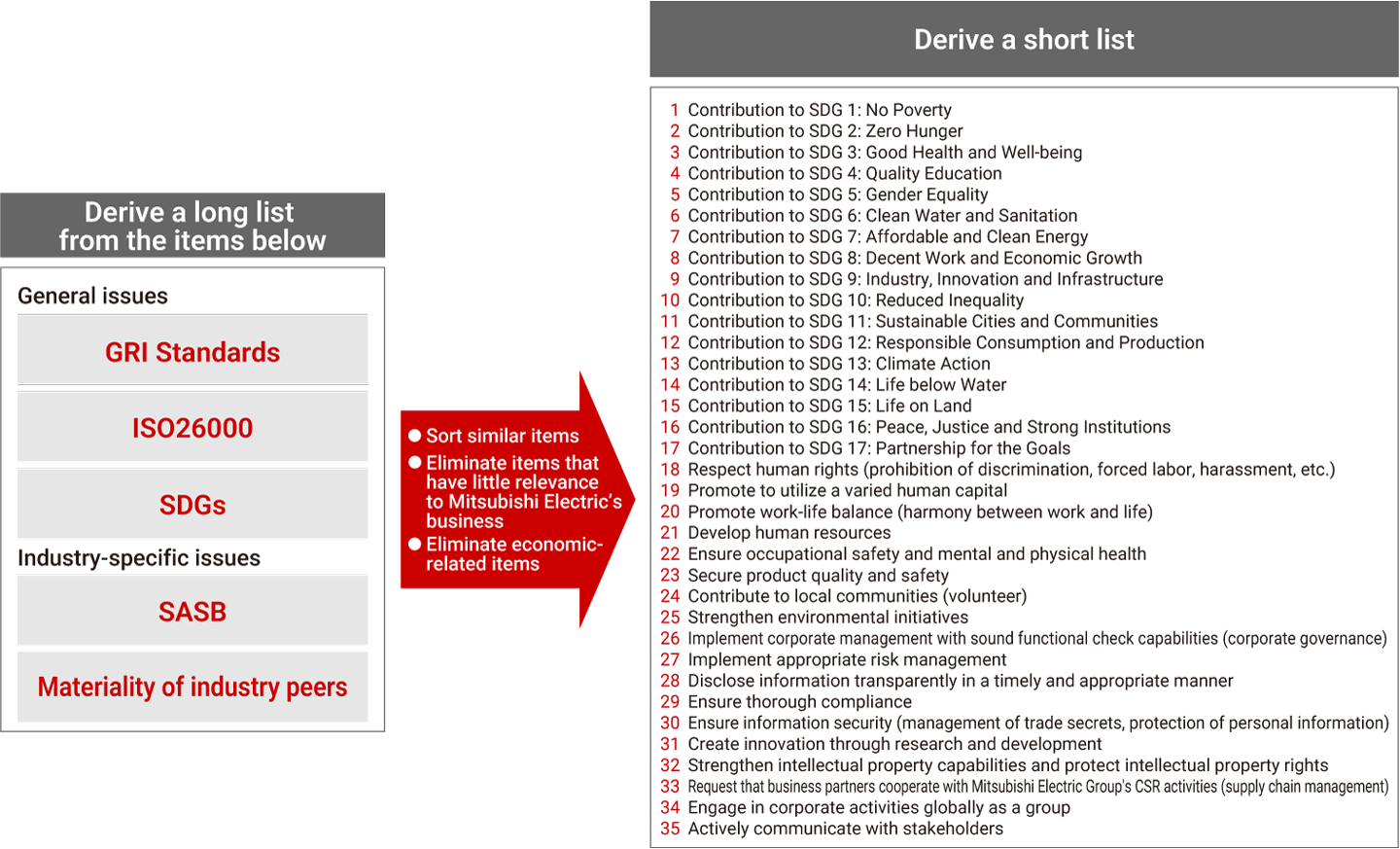
Candidate materiality issues (important challenges) were identified and shortlisted based on ISO26000,*1 the GRI Standards,*2 the SASB standards,*3 and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- 1 Guidelines concerning social responsibility issued by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO)
- 2 International standards for sustainability reporting issued by Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), international NGO.
- 3 Information disclosure rules concerning the environment, society, and governance (ESG) created by the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB), a non-profit organization in the U.S.
 Extraction of candidate materiality from guidelines, etc.
Extraction of candidate materiality from guidelines, etc.
Step 2 Assessment of Internal and External Views and Study of Materiality (FY2021)
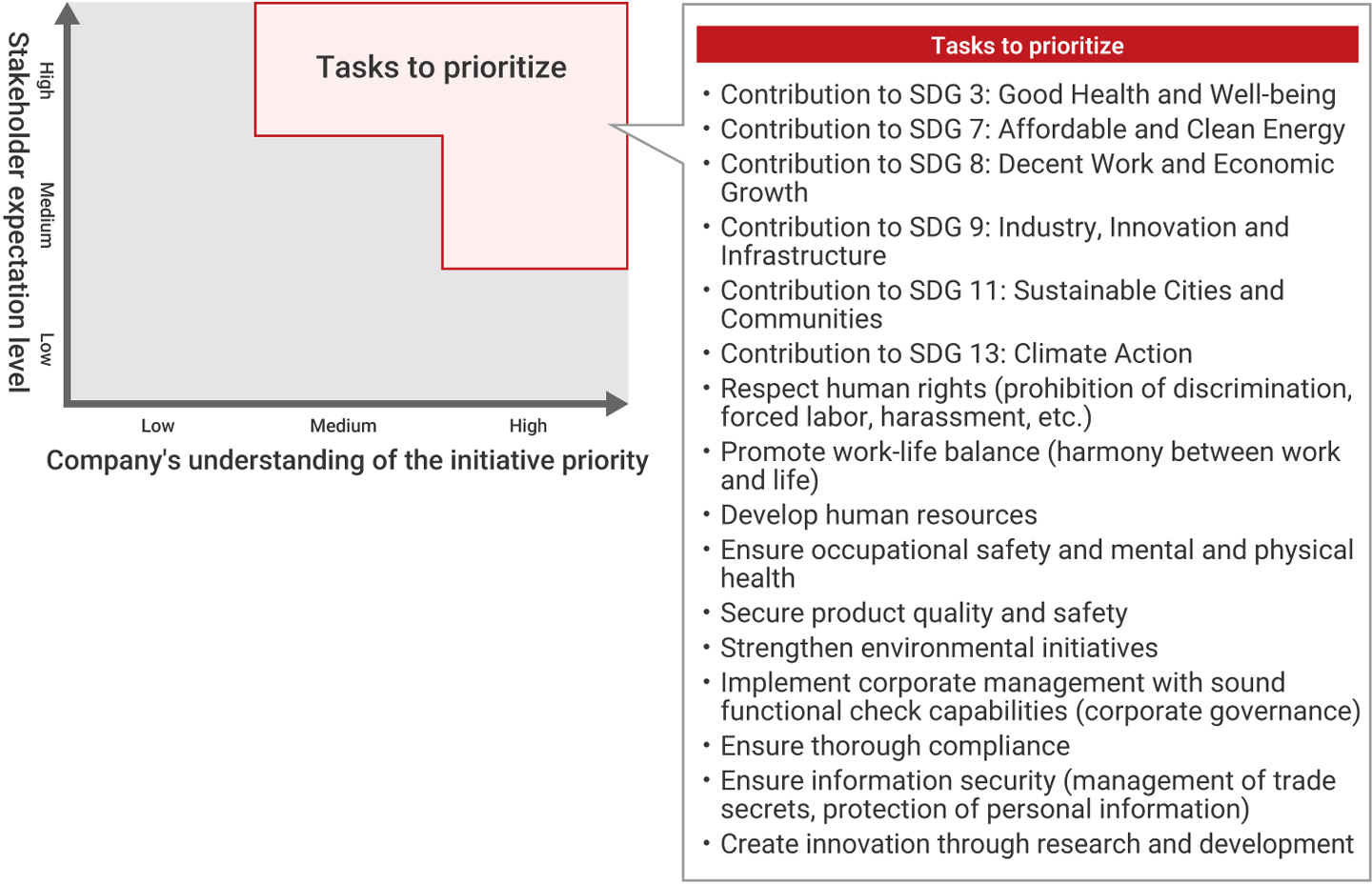
Next, questionnaire surveys were conducted with stakeholders such as consumers, suppliers, investors, and Mitsubishi Electric Group employees to assess their expectations of the Group regarding addressing social issues. In addition, through interviews and dialogues with experts, we gained their views and opinions of the Mitsubishi Electric Group. Based on the results obtained, we narrowed down the issues that needed to be addressed with the highest priority and examined their materiality.
 Mitsubishi Electric’s matrix of materiality
Mitsubishi Electric’s matrix of materiality
Step 3 Identification of Materiality (FY2021)
The issues thus extracted and studied through the above-described process and specific mid- to long-term initiatives and targets/key performance indicators (KPIs) were identified as the Mitsubishi Electric Group’s materiality by the Sustainability Committee.
Mid- to Long-Term Initiatives, Goals for Fiscal 2026, and Results for Fiscal 2025
Each fiscal year, the Mitsubishi Electric Group sets goals and key performance indicators (KPIs) for addressing materiality issues, with the Sustainability Committee confirming and promoting progress of these goals as the Group works to enhance corporate value.
