Risk Management
Basic Policy
With overseas revenue accounting for over 50% of the total, the Mitsubishi Electric Group seeks to transform into a “Circular Digital-Engineering” Company in a wide range of business areas. We also take the various compliance incidents that have come to light seriously, and we have been working to improve our internal control system and others.
To fulfil the Group’s responsibility to all stakeholders, including the general public, customers, shareholders, and employees, and to achieve sustainability, we appropriately manage risks associated with the conduct of our business while strengthening internal control systems with an emphasis on prevention. Specifically, the framework incorporates risk management into business activities, allowing risks to be managed according to the size and characteristics of each business. Significant risks common to the entire Group are managed and prioritized according to their impact on the management of the Group as a whole.
For new risks in economic security, technological innovations including AI, and fields such as sustainability, etc., we will respond in an effective manner by employing cross-organizational and flexible team approaches.
Risk Management Framework
The Group, in addition to each division and domestic and overseas affiliates independently carrying out risk management, has established a Risk Management system that enable appropriate and quick decision-making where Mitsubishi Electric’s each corporate division (division in charge of risk management) supervises and assesses each division and domestic and overseas associated companies in their respective specialized areas, and CRO (Chief Risk Management Officer) and a Corporate Legal & Risk Management Group supervise the entire Group.
While assigning priority to various types of risks according to their impact on the management of the entire Group, we will make management decisions at the Risk Management Compliance Committee Meetings and proceed with them in a flexible and strategic manner, not only in response to conventional risks such as large-scale disasters and social risks, but also in exploration of and preparedness for new risks in economic security, technological innovations including AI, and fields such as sustainability, etc. In particular, important matters related to management supervision and execution are deliberated upon and decided at the Board of Directors meetings and the Executive Officers' meetings.
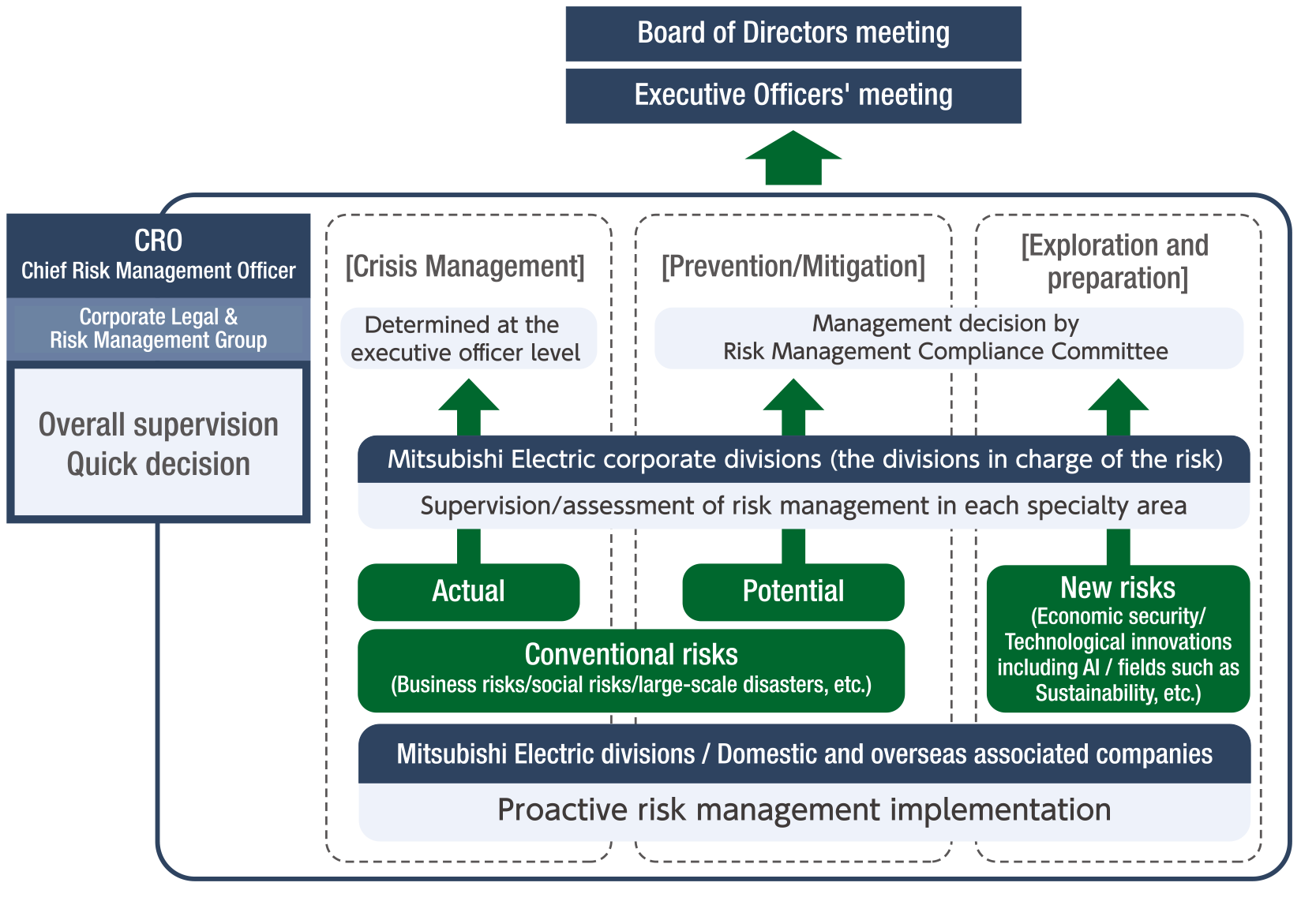 Risk management framework (Mitsubishi Electric Group)
Risk management framework (Mitsubishi Electric Group)
Disaster Countermeasures
Development of a Response Framework for Large-scale Disasters
The Mitsubishi Electric Group has established a Risk Management and Compliance Committee chaired by the Chief Risk Officer (CRO) and conducts regular verification and review of the business continuity plan (BCP), including the Group’s disaster countermeasures, at least once a year.
In the event that any of the Mitsubishi Electric Group’s sites suffer or are at risk of suffering serious damage as the result of a large-scale disaster, we will establish the Mitsubishi Electric Emergency Response Center, headed by our president, which will serve as the central hub for the entire Mitsubishi Electric Group in responding to the emergency situation. In addition to verifying the (personal and physical) disaster situation, the Emergency Response Center will promptly examine and execute policies in response to business continuity initiatives and requests from society (support for affected areas, donations, etc.). Particularly with regard to overseas sites and associated companies overseas, it will work closely with each regional response headquarters to ensure employee safety (safety confirmation, livelihood support, etc.) and provide support for business restoration.
 Mitsubishi Electric Group’s disaster prevention framework
Mitsubishi Electric Group’s disaster prevention framework
Initiatives for Business Continuity
Business continuity plan (BCP) Formulation and Regular (Annual) Review
To fulfill our responsibility as a product supplier, we had all Mitsubishi Electric Group offices formulate a BCP assuming the possible outbreak of a new strain of influenza in fiscal 2011 and a BCP assuming the risk of a large-scale earthquake in fiscal 2013 and urged major associated companies in Japan and overseas to formulate a BCP.
Each office and associated company in Japan and overseas where the BCP has been established, reviews it and upgrades countermeasures every year so that the BCP once developed will not turn into a mere formality.
Business Continuity in the Supply Chain
At Mitsubishi Electric, we pursue initiatives to avoid situations in which a large-scale disaster or other unavoidable circumstance imposes serious damage on suppliers, severs the supply of materials, or obstructs our production activities
Activities for Visualizing the Procurement Parts Supply Chain and Mitigating Procurement Risks in Addition to Procurement
To prepare for the risk of supply chain disruptions in the event of an emergency, we implement various measures, such as visualizing the supply chain per procured item and purchasing from multiple suppliers. In addition, we continue to educate and support our suppliers on disaster preparedness by holding BCP seminars for them.
Activities for Ensuring a Prompt Initial Response and Efficient Response Tasks in Times of Emergency
We are restructuring our frameworks and systems to accelerate and streamline operations, including centralized management of supply chain information for purchased goods, supplier impact surveys in the event of an emergency, and automation of response tabulation.
Strengthening Disaster Responses
Each office and associated companies of the Mitsubishi Electric Group possesses a disaster response manual that is used to implement preliminary measures (disaster mitigation measures) and disaster prevention drills.
For example, Mitsubishi Electric carries out an emergency drill and safety confirmation training that involves the use of a safety confirmation system at each site. In addition, we have two separate data centers in Tokyo and the Kansai region and carry out an annual drill for switching between data centers in the event of an emergency.
We have also instructed associated companies to establish the same level of disaster countermeasures as those implemented by Mitsubishi Electric to strengthen their emergency preparedness through disaster-prevention drills at each site.
Pandemic Countermeasures
The development of various modes of transportation and transportation networks, and the globalization of the economy have increased not only the movement of people, but also the risk of pandemic diseases such as the Ebola virus disease and new strains of influenza.
At the Mitsubishi Electric Group, we are working hard to fulfill our corporate social responsibilities while advancing the globalization of our business. Toward this end, we have commenced initiatives in Japan to (1) ensure people’s safety, (2) sustain businesses that serve societal functions, and (3) minimize economic impact on our company in the event of an outbreak of a new strain of influenza (through BCP formulation, keeping tabs on the dynamics of business travelers and expatriates, stockpiling masks, etc.). For our overseas associated companies, we provide direction for establishing countermeasures suitable for the situation in each country, including the formulation of a BCP that anticipates the outbreak of a new strain of influenza.
Ensuring Safety Overseas
The Mitsubishi Electric Group’s Overseas Security Center works closely with overseas sites, including local associated companies and overseas offices of Mitsubishi Electric and associated companies in Japan, to grasp the dynamics and confirm the safety of overseas business travelers, convey various information (travel restrictions, etc., based on information gathered from the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and specialized agencies), and to provide employee education.
In addition, from the perspective of geopolitical risks, each overseas site prepares a crisis management manual that outlines evacuation procedures and routes in the event of an emergency, collects relevant risk information from overseas crisis management consultants and other sources on a weekly basis, and shares it with relevant personnel.
We also participated in the public-private overseas safety cooperation conference sponsored by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and exchanged information and views with other companies and organizations. The results of the conference have been incorporated into the risk management activities of our company and overseas sites.
Economic Security
In recent years, there has been rising tension in the international community driven by the struggle between the United States and China for technological supremacy, the prolonged Russian invasion of Ukraine, and the conflict between Palestine and Israel that is spreading throughout the Middle East. As a result, risk management that incorporates the required control measures has become necessary. In particular, a comprehensive understanding of the background and intentions of policies and regulations and the practice of risk management that includes involvement in rule-making have become important in responding to the introduction of systems by individual countries that go beyond the export controls based on the international agreements of the past (in areas such as investment, procurement, development, human resources, networks, and data management), as well as demands to address forced labor and environmental problems in the supply chain.
Moreover, to ensure business continuity in response to the risks of supply chain disruptions and interruptions to the supply of critical commodities caused by geopolitical risks, it is essential to identify vulnerable items and commercial distribution channels as well as to strengthen supply chains through appropriate risk control.
In order to keep up with the dynamic changes in the economic security environment, the Mitsubishi Electric Group has established the Corporate Economic Security Division. We have also created a groupwide economic security system by setting up the Economic Security Secretariat in each business site and business group, the Economic Security Office in associated companies in Japan, and the Economic Security Administrator in associated companies overseas.
This system enables us to investigate and analyze technologies, policy trends, and legal systems related to security. It also assists us with the integrated management of four aspects of economic security from a comprehensive perspective. These four are: group-wide information management; supply chains; industry policies; and ESG and social ethics.
The four aspects of economic security considered by Mitsubishi Electric
| Sensitive technology and information management |
|
|---|---|
| Supply chain management |
|
| Industry policy |
|
| Challenges that have not been considered security issues (ESG, social ethics |
|
